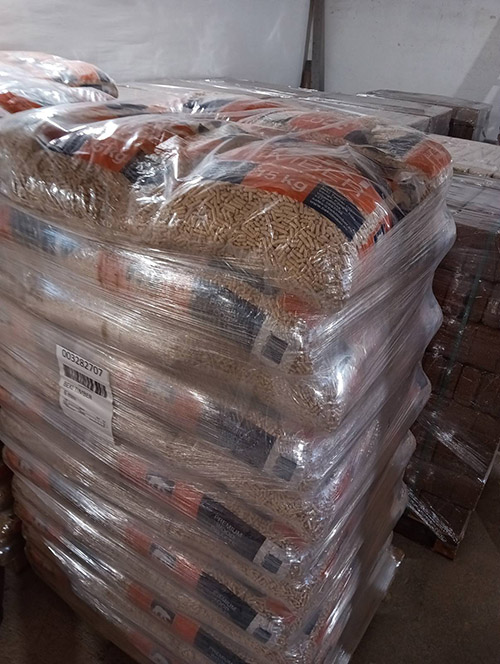
Pellets
Pellets "Premium"
The Use of Pellets
Pellets are a popular fuel choice thanks to their strong environmental benefits, coal-like calorific value, and affordability. They are commonly used in automated residential and industrial boiler systems.
Countries like Austria, Denmark, and Sweden, which lead in the production of innovative energy sources, have embraced pellets extensively. Their low moisture content (7–10%) makes them highly effective for use in pyrolysis boilers with minimal refinement.
Technical Specifications
- Density: 1.5 (sinks in water)
- Calorific Value: 5 kWh per kilogram. However, this figure may vary depending on the efficiency of the combustion equipment. For comparison, pellets have 1.5 times the calorific value of traditional firewood.
Environmental Benefits of Pellets
Pellets align seamlessly with the natural carbon cycle. Unlike coal and conventional energy sources, the CO₂ released during pellet combustion equals the amount absorbed by the wood during its growth. This "closed carbon loop" means that the CO₂ emissions are no greater than they would be if the wood were to decompose naturally.
Using pellets also prevents pollution from wood-processing waste and reduces the need for logging live forests. Additionally, pellets contain very low levels of sulfur, resulting in minimal sulfur dioxide emissions and reducing the likelihood of acid rain.
Other Advantages of Pellets
Unlike coal or diesel fuel, burning pellets does not produce unpleasant odors, and the smoke is nearly colorless. Furthermore, pellets outperform liquid fuels and coal in terms of reduced harmful emissions, making them an eco-friendly choice that benefits the environment.